-
Original Articles
-
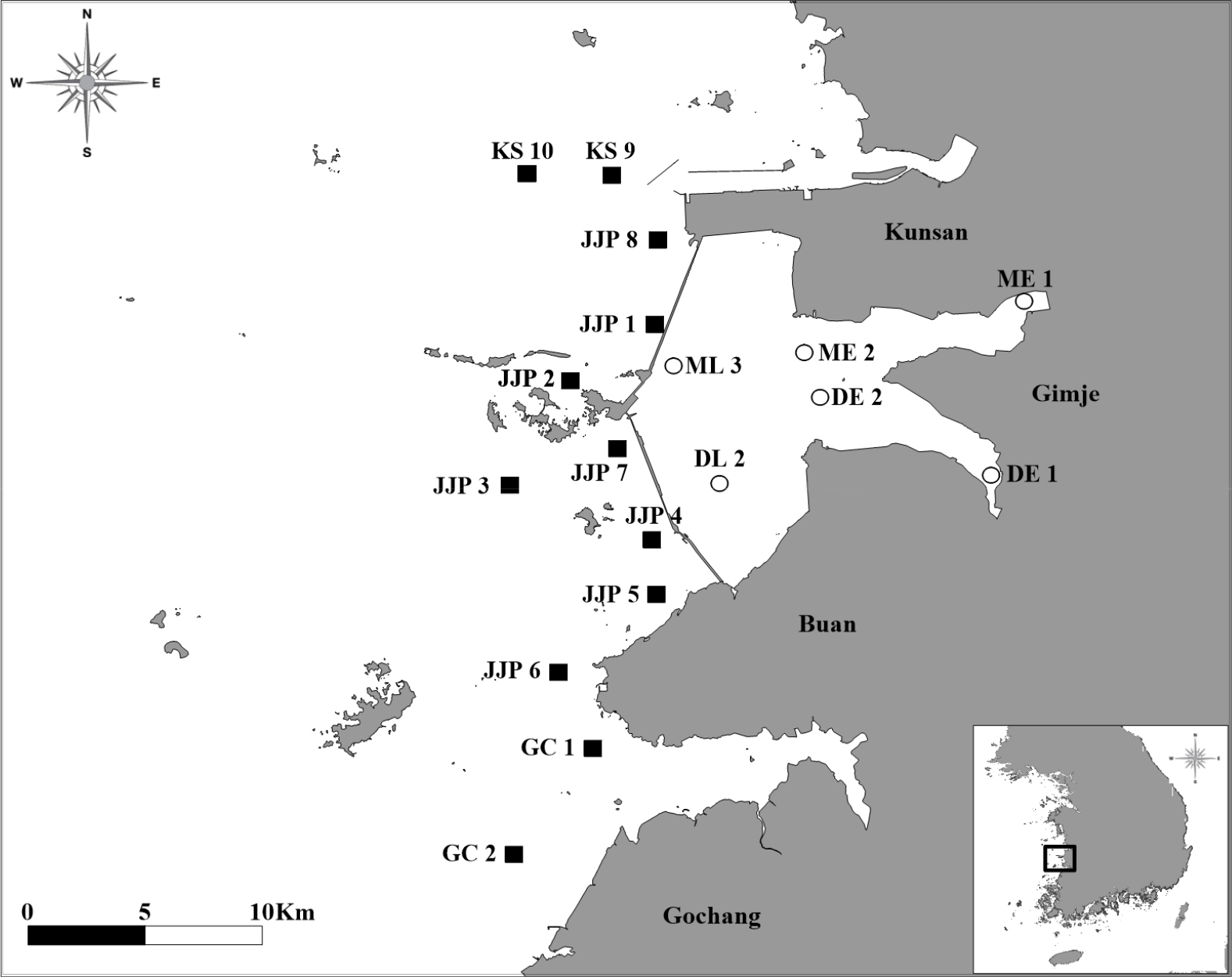
Correlation between Pyropia Production and Environmental Factors in Saemangeum Sea Area
새만금 해역에서의 김 생산량과 환경인자의 상관관계 연구
-
Ji Hong Chae, Jaeseong Kim, Young Sik Kim
채지홍, 김재성, 김영식
- To understand the effects of environmental factors on the quantitative fluctuations of farmed Pyropia spp. in the Saemangeum Sea area, we analyzed …
새만금 해역에서 생산되는 양식 김(Pyropia spp.)의 양적 변동에 환경인자가 미치는 영향을 이해하기 위해, 해양환경정보시스템을 활용한 수질 변화를 분석하였다. 분석 결과, 엽록소- …
- To understand the effects of environmental factors on the quantitative fluctuations of farmed Pyropia spp. in the Saemangeum Sea area, we analyzed changes in water quality using the Marine Environment Information System. Our findings indicate that the concentration of chlorophyll-a has been increasing, whereas the concentrations of dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN) and dissolved inorganic phosphate (DIP), which are essential for Pyropia growth, have gradually decreased. Similarly, both total nitrogen (T–N) and total phosphate (T–P) have also shown a decreasing trend. A significant decline in Pyropia production was observed in 2015, including reductions in total production, yield per chaek (yield per unit area), and sales revenue. A more detailed analysis of water quality in November 2014 and February 2015 revealed that DIN and DIP concentrations were significantly lower than the 21-year average and approached the threshold levels associated with Pyropia chlorosis. This suggests that reduced levels of dissolved inorganic nutrients may have played a significant role in the decreased Pyropia production in 2015. However, because similar nutrient conditions in other years did not cause production problems, it is difficult to attribute changes in Pyropia production solely to nutrient concentrations. Therefore, future studies on Pyropia production should consider not only the influence of the marine environment but also management factors such as pest outbreaks, chlorosis, and farming density.
- COLLAPSE
새만금 해역에서 생산되는 양식 김(Pyropia spp.)의 양적 변동에 환경인자가 미치는 영향을 이해하기 위해, 해양환경정보시스템을 활용한 수질 변화를 분석하였다. 분석 결과, 엽록소-a의 농도는 증가하는 반면, 김 생장에 필수적인 용존 무기질소(DIN)와 용존 무기인(DIP)의 농도는 점차 감소하는 것으로 나타났다. 마찬가지로, 총질소(T–N)와 총인(T–P) 농도도 감소 경향을 보였다. 2015년에는 김 생산성이 크게 감소하였으며, 총 생산량, 책 단위당 수확량, 생산액 모두 감소하였다. 2014년 11월과 2015년 2월의 수질을 분석한 결과, DIN과 DIP의 농도는 최근 21년 간의 평균 값에 비해 현저히 낮았으며, 김의 황백화 현상과 관련된 임계치에 근접하였다. 이는 용존 무기 영양염류의 감소가 2015년 김 생산성 감소에 중요한 역할을 했을 수 있음을 시사한다. 그러나 다른 해에도 유사한 영양염 조건이 나타났음에도 불구하고 생산성 문제가 발생하지 않은 점을 고려할 때, 김 생산성 감소를 영양염 농도만으로 단정하기는 어렵다. 따라서 김의 생산성은 당해 해양환경의 영향과 갯병 발생, 황백화, 양식밀도 등 관리 측면도 고려한 연구가 필요할 것으로 사료된다.
-
Correlation between Pyropia Production and Environmental Factors in Saemangeum Sea Area
-
Original Articles

- First Record of Adult Halicampus punctatus off Jeju Island, Korea
- Sihyun Park, Sung Kim
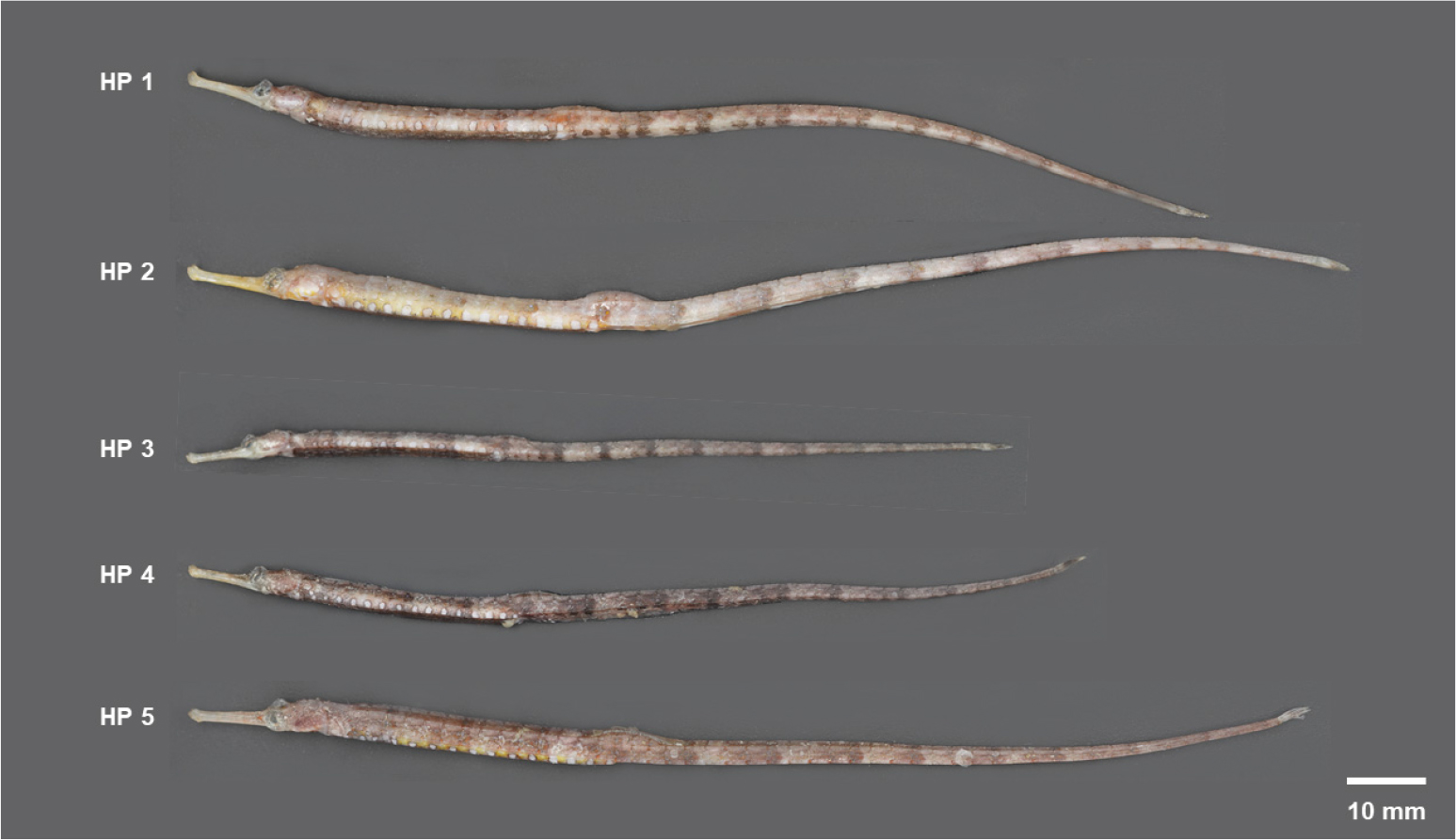
- Although larval stages of the starry pipefish, Halicampus punctatus, have previously been documented in the waters surrounding the Korean Peninsula, adult …
- Although larval stages of the starry pipefish, Halicampus punctatus, have previously been documented in the waters surrounding the Korean Peninsula, adult specimens have not yet been confirmed. Here, we report the first collection of five adult specimens from the eastern waters off Jeju Island and identify them using both morphological characters and COI sequence analysis. The specimens were identified as H. punctatus based on morphological features consistent with previous descriptions. The COI distance and maximum-likelihood (ML) analyses demonstrated that the present Korean specimens formed a clade with H. macrorhynchus, diverging from other members of the genus. This phylogenetic configuration directly challenges the monophyly of the genus Halicampus and necessitates a taxonomic revision. - COLLAPSE
-
Original Articles
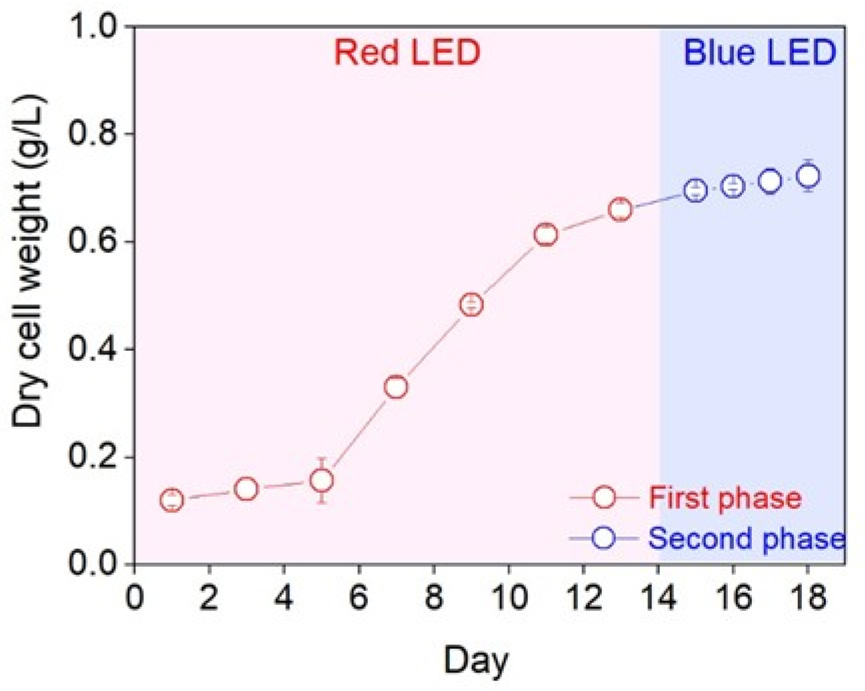
- Comparative Analysis of Two-Phased and Mixed LED Light Cultures for Enhancing Carbohydrate, Protein, and Lipid Production in Chlorella vulgaris PKVL7422
- Ji Seung Han, Seungjin An, Woojoo Shin, Tae-Jin Choi, Seok Jin Oh
- Microalgae, such as Chlorella vulgaris, play a crucial role in aquatic ecosystems and have substantial industrial value because of their ability …
- Microalgae, such as Chlorella vulgaris, play a crucial role in aquatic ecosystems and have substantial industrial value because of their ability to produce various useful substances, including lipids and proteins. This study aimed to determine the more efficient culture system for improving the biochemical composition of C. vulgaris PKVL7422 by comparing two-phased (TPLC) and mixed LED light culture (MLC) systems using blue (λmax=450 nm) and red (λmax=660 nm) light. In the TPLC system, the highest protein and lipid contents were observed on day 17 of the second phase under blue light, with 1.5-fold and 1.6-fold increases in protein and lipid, respectively, compared to the first phase under red light. However, no significant difference was observed in the biological compositions compared to those measured during the stationary phase under monochromatic blue light. In the MLC system, a red-to-blue light ratio of 3:7 yielded higher protein and lipid contents than the other ratios. Notably, the protein content under these conditions was 1.7 times higher than the highest content observed on day 17 of TPLC. Thus, strains such as PKVL7422 may improve the efficiency and productivity of the biological composition through the MLC method using a 3:7 (red: blue) ratio. - COLLAPSE


 Aquatic Nature
Aquatic Nature